Introduction:
In the world of finance and investments, the Ten-Year Treasury bond holds a special place. As a benchmark for long-term interest rates, it plays a crucial role in shaping the global economy, impacting everything from government borrowing costs to mortgage rates and corporate financing. This article will delve into the significance of the Ten-Year Treasury bond, its role in the financial markets, and its broader implications for investors and economies around the world.
Understanding The Ten-Year Treasury Bond
The Ten-Year Treasury bond is a fixed-income security issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. It has a maturity period of ten years and pays interest semi-annually until maturity. Investors are attracted to these bonds because they are considered low-risk, backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. As such, they are often viewed as a safe haven for investors during times of economic uncertainty.
The Importance Of The Ten-Year Treasury Yield
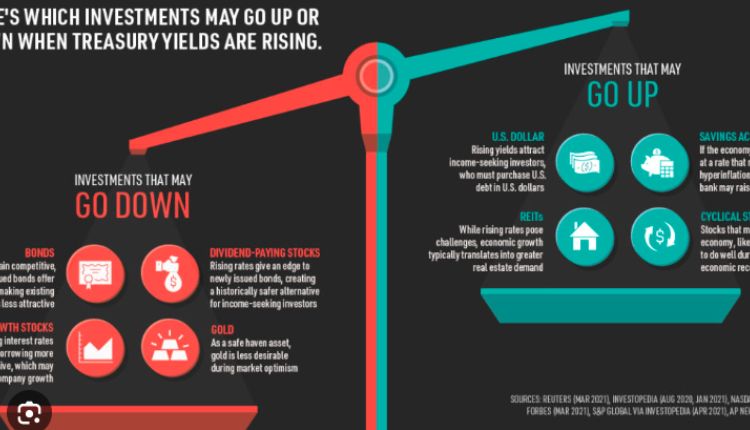
The yield of the Ten-Year Treasury bond is closely watched by investors, economists, and policymakers. It serves as a key indicator of investor sentiment and economic expectations. When the economy is thriving, investors might be more inclined to pursue riskier assets, leading to lower demand for Treasuries and, consequently, a higher yield. Conversely, during economic downturns, the demand for Treasuries tends to increase, driving their prices up and yields down.
Impact On Interest Rates
The Ten-Year Treasury yield heavily influences interest rates across various financial products, including mortgages, corporate bonds, and savings accounts. As it represents the benchmark for long-term borrowing costs, changes in the Ten-Year Treasury yield can have a cascading effect on other interest rates. For instance, when the yield rises, borrowing costs for mortgages and business loans tend to follow suit, potentially dampening economic activity.
- Relationship with Inflation Inflation plays a significant role in the Ten-Year Treasury bond’s performance. When inflation expectations rise, investors demand higher yields to compensate for the loss of purchasing power over time. Consequently, the Ten-Year Treasury yield tends to move in tandem with inflation expectations. Central banks closely monitor this relationship when formulating monetary policy to maintain price stability and support economic growth.
- Global Impact and Safe-Haven Status The Ten-Year Treasury bond’s safe-haven status extends beyond U.S. borders. During times of geopolitical turmoil or global financial crises, international investors seek refuge in U.S. Treasuries, leading to increased demand and lower yields. This dynamic has far-reaching effects on global financial markets, as it can influence capital flows, exchange rates, and emerging market economies’ stability.
- Implications for Investors For investors, understanding the Ten-Year Treasury bond’s dynamics is essential for making informed decisions. Those seeking stability and income may find these bonds attractive, especially during uncertain economic climates. However, in periods of economic expansion and higher interest rates, alternative investments may offer more favorable returns.
Conclusion:
The Ten-Year Treasury bond stands as a linchpin in the world of finance, serving as a barometer of economic health and investor sentiment. Its influence extends well beyond the United States, impacting global economies and financial markets. As we navigate through the ever-changing landscape of finance and investment, an understanding of the Ten-Year Treasury’s significance becomes increasingly critical for investors, policymakers, and individuals alike.
FAQs:
FAQ 1: Why is the Ten-Year Treasury bond considered a safe-haven asset? Answer: The Ten-Year Treasury bond is backed by the U.S. government, which is considered one of the most creditworthy entities globally. During times of economic uncertainty or market turbulence, investors seek refuge in assets perceived as safe havens. As a result, they increase their demand for Treasuries, driving up prices and lowering yields, making it an attractive option for risk-averse investors.
FAQ 2: How does the Ten-Year Treasury yield impact mortgage rates? Answer: Mortgage rates tend to follow the movements of the Ten-Year Treasury yield. When the yield rises, mortgage rates also increase, and vice versa. This relationship is due to the fact that both the Ten-Year Treasury yield and mortgage rates are influenced by similar factors, such as inflation expectations and changes in the broader economic environment.